Gonorrhoea (Neisseria gonorrhoea)
Gonorrhoea (Neisseria gonorrhoea)
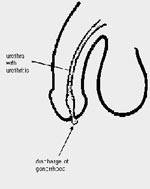
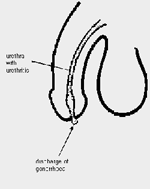 Like Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea is one of the most prevalent Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) in today's society. It can be a devastating disease if left untreated, causing various problems. Unfortunately in as many of 80% of women who contract this disease are without symptoms. This is why so many complications can arise from having gonorrhoea.
Like Chlamydia, Gonorrhoea is one of the most prevalent Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) in today's society. It can be a devastating disease if left untreated, causing various problems. Unfortunately in as many of 80% of women who contract this disease are without symptoms. This is why so many complications can arise from having gonorrhoea.So what is it?
It is a bacterial infection, which is passed on through sexual intercourse that infects the internal genital tract organs e.g. the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries. Sometimes there are symptoms, but as mentioned before a high percentage infected are asymptomatic (no symptoms).
If the disease goes untreated complications in females include adhesions, which form on the fallopian tubes and can result in infertility. If the woman is pregnant, gonorrhoea can be passed on to the baby and can also cause the baby to be born blind.
In both males and females a type of arthritis can occur (gonococcal arthritis) causing crippling joint pain and swelling. Fatal septicemia (infection in the blood stream) is another complication that can occur if this disease goes untreated.
What are the symptoms?
If the individual if to suffer symptoms these may include:
Women
- Increase in vaginal discharge
- Pain on urination
- Irritation of the anus
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
Men
These symptoms are the similar to females, though are more likely to be more severe, however they may also include:
- Discharge from the penis
- Pain on urination
- Irritation of the anus
- Inflamed testicles
- Inflamed prostate gland (size can be examined a by doctor through an anal examination).
Diagnosis
If you have found that you are suffering from similar symptoms such as these, or are informed you have had sex with someone who is suffering from a STD, it is vital you see your doctor immediately. You will need to specifically ask your doctor for an STD test, as pap smears only test for changes in the cervical cells, and not for STDs. A gonorrhoea culture is virtually the same as a standard Pap smear, however the laboratory will be testing especially for this disease. If you are having causal unprotected sex (meaning without using condoms) with different partners, you should ask for this test, along with other STDs when you go in for your annual pap smear, as you may have a STD without symptoms. This is not only reassuring to know you are 'STD free', but if you do have it, it can be treated, and will prevent any further spread of the disease. If your test comes back positive, it is vital that you inform your previous partners, as you are dealing with an infectious disease, and it is important to prevent any further spread (they may be showing no symptoms and also be unaware that they are infected). They may be infecting others. Although this may feel degrading or embarrassing to tell that person you had sex with that they may have this infection, it is important that you do so.
Treatment
This is the easy part. A course of antibiotics will effectively cure gonorrhoea. Hopefully the disease will not have progressed to the point of infertility. You will most likely discover this if you are trying to conceive.
Basically prevention is the best method to avoid the infection of gonorrhoea or any similar STD. Use condoms; they are a 99% effective barrier method in preventing a STD. If you begin a serious relationship (and trust each other) and decide to stop using condoms, it's a good idea to both get HIV and STD tests, so that you both know the only thing you need to worry about is pregnancy. If that's the case make sure you choose the most appropriate contraceptive device.
Louise Ganey
MORE





